BlueSpy is a proof of concept for exploiting vulnerabilities in Bluetooth headsets and eavesdropping on private conversations
BlueSpy是利用蓝牙耳机中的漏洞和窃听私人对话的概念证明
The first results following the publication of BSAM, a security methodology that allows for a complete and homogeneous assessment of Bluetooth devices security, have not been long in coming.
BSAM是一种安全方法,可以对蓝牙设备的安全性进行完整和均匀的评估,其发布后的第一批结果并没有多久。
Its application has helped identify security problems in many Bluetooth headsets, showing that manufacturers must take Bluetooth security seriously to avoid, among other risks, unauthorized connections to these devices attempting to spy on conversations.
它的应用已经帮助识别了许多蓝牙耳机中的安全问题,这表明制造商必须认真对待蓝牙安全,以避免未经授权连接到这些设备试图监视对话等风险。
Using a Python script from Linux, automating the tasks required to exploit a common vulnerability in Bluetooth devices is possible. This vulnerability allows anyone to access the Bluetooth device without alerting or notifying the owner, i.e., entirely silently.
使用来自Linux的Python脚本,可以自动执行利用蓝牙设备中常见漏洞所需的任务。此漏洞允许任何人访问蓝牙设备,而无需提醒或通知所有者,即,完全安静地
The demonstration focused on a particular high-end headset. Still, it became clear that headsets from other manufacturers are also affected by the same vulnerability, as the device only needs to support “JustWorks” pairing.
演示集中在一个特定的高端耳机。尽管如此,很明显,其他制造商的耳机也受到相同漏洞的影响,因为该设备只需要支持“JustWorks”配对。
At the RootedCon Madrid 2024 security conference, Tarlogic presented BSAM and its research, demonstrating how to capture audio without the device user’s awareness and use it to eavesdrop on private conversations.
在RootedCon马德里2024安全会议上,Tarlogic展示了BSAM及其研究,演示了如何在设备用户不知情的情况下捕获音频,并利用它来窃听私人对话。
This open and collaborative methodology incorporates controls that assess the security of multiple aspects of Bluetooth communications and provides examples of vulnerabilities in this technology, which is widely used in mobile and low-power devices.
这种开放和协作的方法结合了评估蓝牙通信多个方面安全性的控制措施,并提供了该技术中漏洞的示例,该技术广泛用于移动的和低功耗设备。
Vulnerability identification using BSAM
使用BSAM识别漏洞
The methodology is divided into seven sections, representing the phases during an audit and addressing a Bluetooth device’s security aspects.
该方法分为七个部分,代表审计期间的各个阶段,并解决蓝牙设备的安全问题。
One of these sections is the inter-device discovery phase, in which devices broadcast and exchange announcement messages with information about the device’s identity and capabilities.
这些部分之一是设备间发现阶段,在该阶段中,设备广播并交换具有关于设备的身份和能力的信息的通知消息。
Among the security controls built into the discovery phase, it is particularly relevant to check the exposed name, the point at which the device is discoverable and the use of random MAC addresses.
在发现阶段内置的安全控制中,检查暴露的名称、设备可验证的点以及随机MAC地址的使用尤其重要。
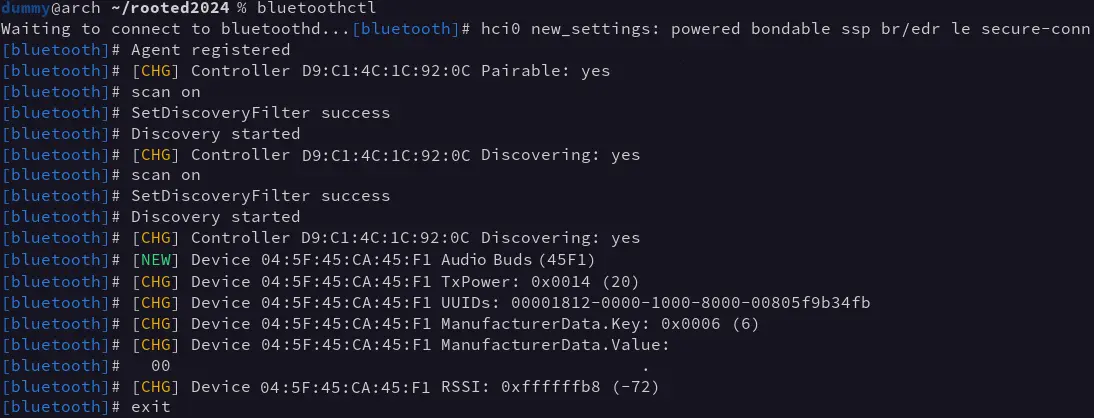
In our case, the headsets are exposed to their name in the Bluetooth announcement messages, which immediately identify them.
在我们的情况下,耳机在蓝牙公告消息中显示其名称,这会立即识别它们。
On the other hand, the headsets use a public, static MAC address, which uniquely identifies them and makes their manufacturer easily identifiable.
另一方面,耳机使用一个公共的静态MAC地址,可以唯一地识别它们,并使其制造商易于识别。
Combining these factors makes a device easily identifiable as a target for an attack such as the one presented. It makes it possible to search for additional information, such as the specific model and whether it has a microphone.
结合这些因素,使设备很容易被识别为攻击的目标,如一个提出。它可以搜索其他信息,例如特定型号和是否有麦克风。
Although the issues identified during the device discovery phase do not seem particularly relevant, they help direct the audit during the next phase of BSAM analysis: pairing.
虽然在设备发现阶段发现的问题似乎并不特别相关,但它们有助于指导BSAM分析的下一阶段(配对)的审核。
Pairing is the process during which two Bluetooth devices generate a shared key. This key will be used to encrypt the link and authenticate both devices going forward. Without the shared key, the devices will typically not allow the connection to continue or will only allow limited interaction with each other.
配对是两个蓝牙设备生成共享密钥的过程。此密钥将用于加密链路并验证两个设备。在没有共享密钥的情况下,设备通常将不允许连接继续或者将仅允许彼此之间的有限交互。
The BSAM controls referred to the pairing stage check the security level during this procedure and the protection of the generated shared key. The security level of the pairing depends on the level of control the user has over the process. At the highest level of security, the user must enter a pin on both devices involved so that only devices explicitly authorized by the user can be paired.
涉及配对阶段的BSAM控制在此过程中检查安全级别以及对生成的共享密钥的保护。配对的安全级别取决于用户对过程的控制级别。在最高级别的安全性下,用户必须在涉及的两个设备上输入PIN,以便只有用户明确授权的设备才能配对。
For ease of use, Bluetooth implements an insecure pairing mechanism called “JustWorks”. This mechanism does not require any verification or notification to the user and allows any device to pair unattended and interact with it.
为了便于使用,蓝牙实现了一种称为“JustWorks”的不安全配对机制。这种机制不需要对用户进行任何验证或通知,并允许任何设备在无人值守的情况下配对并与之交互。
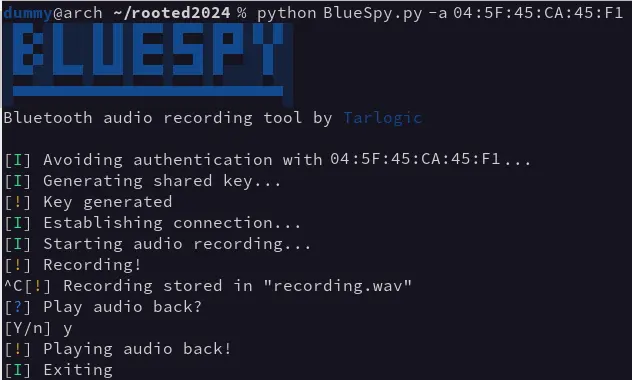
BlueSpy exploits the fact that the “JustWorks” mechanism can be used during pairing, which does not require secure pairing. In combination with a discoverable device in pairing mode, anyone using BlueSpy can initiate the pairing, set a shared key, connect to the headset, and start using it as if it were a legitimate user. In this case, they can activate the microphone and eavesdrop on conversations.
BlueSpy利用了在配对过程中可以使用“JustWorks”机制的事实,这不需要安全配对。与配对模式下的可解锁设备相结合,任何使用BlueSpy的人都可以启动配对,设置共享密钥,连接到耳机,并开始使用它,就像它是合法用户一样。在这种情况下,他们可以激活麦克风并窃听对话。
The BlueSpy script BlueSpy脚本
BlueSpy is a Python script developed as a proof-of-concept exploit for this vulnerability. It only needs native Bluetooth tools available on Linux operating systems.
BlueSpy是一个Python脚本,作为此漏洞的概念验证攻击而开发。它只需要Linux操作系统上可用的本机蓝牙工具。
An Arch Linux distribution has been used with a working installation of BlueZ, the Linux Bluetooth stack, and PipeWire as an audio server to record and playback the captured audio.
Arch Linux发行版已与BlueZ、Linux蓝牙堆栈和PipeWire的工作安装一起使用,PipeWire作为音频服务器来记录和回放捕获的音频。
The BlueSpy tool, with code and documentation, is published in Tarlogic Security’s GitHub repository.
BlueSpy工具及其代码和文档发布在Tarlogic Security的GitHub存储库中。
To execute the attack against a device, you need to know its Bluetooth MAC address, which can be obtained with any Bluetooth scanning tool, in our case using bluetoothctl:
要对设备执行攻击,您需要知道其蓝牙MAC地址,可以使用任何蓝牙扫描工具获得,在我们的情况下使用bluetoothctl:
Once the MAC address of the device has been obtained, you can run BlueSpy, which performs the following steps to execute the attack:
一旦获得设备的MAC地址,您就可以运行BlueSpy,它将执行以下步骤来执行攻击:
- Initial configuration 初始配置
- Pairing (generation of shared key)
配对(生成共享密钥) - Connection 连接
- Audio recording 音频记录
- Audio playback 音频回放
During the configuration stage, the script ensures that the local computer will allow pairing and key sharing with remote devices, which can be done without security. In other words, it ensures that “JustWorks” can be used to prevent the user from being notified or having to interact.
在配置阶段,脚本确保本地计算机将允许与远程设备配对和密钥共享,这可以在没有安全性的情况下完成。换句话说,它确保“JustWorks”可以用来防止用户收到通知或不得不进行交互。
Once configured, the pairing is performed, and the generated key is stored in the BlueZ device database, which is usually located in the “/var/lib/bluetooth” directory.
一旦配置完成,配对就会执行,生成的密钥会存储在BlueZ设备数据库中,该数据库通常位于“/var/lib/bluetooth”目录中。
With the generated and stored key, a connection to the device can be initiated using bluetoothctl. The PipeWire sound server automatically enables a new audio source to be added to the system (audio source).
使用生成并存储的密钥,可以使用bluetoothctl发起与设备的连接。PipeWire声音服务器自动启用要添加到系统的新音频源(音频源)。
BlueSpy uses this new audio source to record and store it in a file (“recording.wav” by default). This recording can then be played back with “paplay” or any other audio playback tool.
BlueSpy使用这个新的音频源录制并存储在文件中(默认情况下为“recording.wav”)。然后可以使用“paplay”或任何其他音频播放工具播放此录音。
Mitigation 缓解
The fundamental reason BlueSpy works is that the headset doesn’t require secure pairing. The most straightforward mitigation requires the user to allow pairing explicitly using a physical button or by playing an audio notification when a new pairing attempt is received.
BlueSpy工作的根本原因是耳机不需要安全配对。最直接的缓解措施要求用户使用物理按钮或在收到新的配对尝试时播放音频通知来明确允许配对。
Another possible mitigation is using a physical button or control to turn on or off the device’s discoverability and pairing state so that the user can control it when it is in each mode of operation.
另一种可能的缓解是使用物理按钮或控件来打开或关闭设备的可扩展性和配对状态,使得用户可以在设备处于每种操作模式时对其进行控制。
The device manufacturer must implement all of these mitigations, but users can also protect themselves by incorporating safe practices into their everyday use of Bluetooth technology.
设备制造商必须实施所有这些缓解措施,但用户也可以通过将安全实践纳入蓝牙技术的日常使用中来保护自己。
There are headsets that are not discoverable, pairable, or connectable when locked in their charging station or when already connected to some other device. One way to avoid these attacks is to keep them locked in their case whenever they are not going to be used.
有些头戴式耳机在锁定在充电站或已连接到其他设备时无法拆卸、配对或连接。避免这些攻击的一种方法是在不使用它们的时候将它们锁定在它们的情况下。
These recommendations, however, may need to be revised for other devices with similar problems, as Bluetooth devices can behave in very different ways. Therefore, it is imperative that Bluetooth devices are audited from a security point of view using, e.g., the BSAM methodology to determine their specific performance.
然而,这些建议可能需要针对其他有类似问题的设备进行修改,因为蓝牙设备的行为方式可能非常不同。因此,从安全的角度来看,必须对蓝牙设备进行审计,例如,BSAM方法来确定其具体性能。
In conclusion 最后
Bluetooth technology offers a simple form of communication for low-power devices, but many manufacturers have prioritized ease and convenience of use by users/customers over security.
蓝牙技术为低功耗设备提供了一种简单的通信形式,但许多制造商将用户/客户使用的易用性和方便性置于安全性之上。
Within companies, to maintain a complete and beneficial security policy, risk calculation must take into account all devices and systems connected to the infrastructure. Until now, risk calculation has focused mainly on devices connected by cable or WiFi, but research and tools such as BlueSpy show that it is essential to consider technologies such as Bluetooth as well. Failure to do so means unwittingly exposing oneself to security vulnerabilities such as the one shown in this article.
在公司内部,为了保持完整和有益的安全策略,风险计算必须考虑连接到基础设施的所有设备和系统。到目前为止,风险计算主要集中在通过电缆或WiFi连接的设备上,但BlueSpy等研究和工具表明,也必须考虑蓝牙等技术。如果不这样做,就意味着在无意中将自己暴露在本文所示的安全漏洞之下。
The BSAM methodology is a tool that simplifies and standardizes the security assessment of Bluetooth devices and allows them to be integrated into the organization’s risk calculation and security policy.
BSAM方法是一种简化和简化蓝牙设备安全评估的工具,并允许将其集成到组织的风险计算和安全策略中。